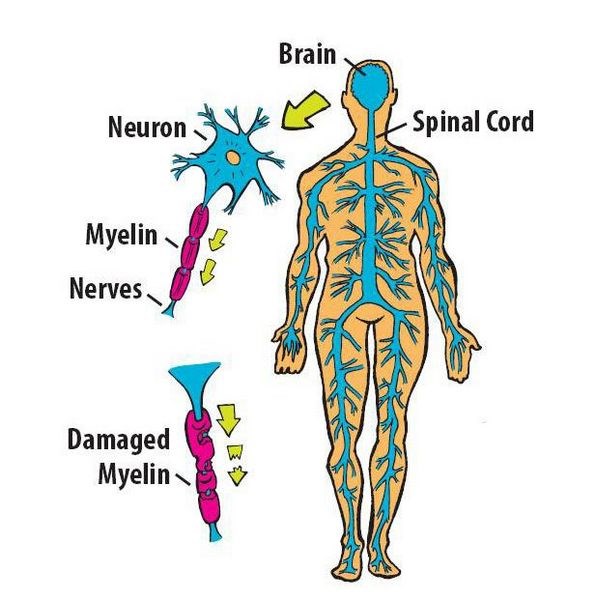
MS is a disease that affects the brain, spinal cord and optic nerve (central nervous system).
When a person has MS, myelin - the covering that protects the nerves in the brain and spinal cord - is damaged.
Damaged myelin may form scar tissue. This scar tissue can block or slow down messages being sent along the nerve fibres. The brain is like a computer that sends messages to your body telling it what to do.
The spinal cord is like a thick cable of wires attached to the computer. Messages travel from the brain, along the spinal cord, to muscles and other parts of the body.
When these messages are distorted or disrupted by MS, a variety of MS-related symptoms may occur.
What is multiple sclerosis (MS)? Symptoms of MS Symptoms of MS are unpredictable and vary greatly from person to person and from time to time in the same person.
Symptoms can include vision problems, numbness, uncoordination or loss of balance, bladder and bowel problems, stiffness of muscles, weakening or paralysis of any part of the body, fatigue, pain, mood or cognitive changes.
MS Facts
MS was discovered in 1868 by French Neurologist Dr. Jean-Martin Charcot
MS is the most common neurological disease affecting young Canadian adults
It is estimated that between 55,000 and 75,000 Canadians are affected by MS
Canada has one of the highest prevalence rates of MS in the world
MS affects women three times as often as men
MS is more prevalent in northern regions like Canada, Great Britain, and the United States
Diagnosis usually occurs in people between the ages 15 to 40 years - the career and family building years
Diagnosing MS can be very difficult
MS is not contagious
There are now drug therapies that are having a significant impact on reducing the
symptoms of MS
Fatigue affects approximately 90 per cent of persons living with MS
Every day, three more people in Canada are diagnosed with MS
Currently, there are 2.5 million people living with MS globally
.png;w=120;h=80;mode=crop)

